Introduction
You may have seen headlines about the counterparty risk that comes into play when cryptocurrency exchanges collapse. Or, maybe you heard about someone who lost the private key to their bitcoin and won’t be able to recover their funds. The rise of cryptocurrencies has introduced new opportunities and challenges in the financial landscape. As digital assets become more integrated into mainstream finance, understanding the management and security of these assets is crucial. Central to this is the choice between custodial and non-custodial wallets. Each type has distinct features, benefits, and risks that influence their suitability depending on user needs and preferences. Learning more about the components, benefits, and risks associated with both custodial and non-custodial wallets may help you more securely manage your cryptocurrency.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Wallet?
A cryptocurrency wallet serves as a digital interface for managing blockchain assets. These wallets store the cryptographic keys essential for accessing digital assets, and they facilitate transactions on a blockchain network. Cryptocurrency wallet holders can securely transfer, receive, and retain their cryptocurrency using their private keys. Understanding its components is crucial for securing and managing these digital assets effectively.
Public Key
A public key in a cryptocurrency wallet functions similarly to a bank account number. When a user generates a wallet, a public key is automatically created to identify the account. This key is used to encrypt messages intended for a specific recipient and can be freely shared with others to receive blockchain assets. Within a blockchain network, these public keys become crucial for the identification and communication process within a blockchain network.

Source: etherscan.io
Private Key
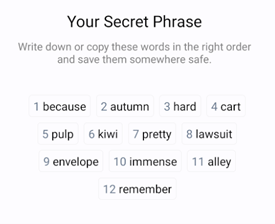
A private key in a cryptocurrency wallet is a crucial cryptographic element that grants the owner full control over their digital assets. Unlike a public key, which can be shared openly, a private key should be kept secure and confidential. A private key is used to authorize transactions and access funds within the wallet through a digital signature that validates the ownership of digital assets on the blockchain. This ensures that only the rightful holder can initiate transfers or other transactions. In addition, private keys utilize a seed phrase, which can be 12 to 24 words long. This secret phrase is important as it is used to back up your private key in case it is lost or forgotten. Users cannot specifically select the words used as part of the seed phrase, so it is essential to secure these secret phrases in a safe location and ensure there are no spelling mistakes. Seed phrases are like passwords but are much harder to remember, which is why it is crucial to secure them properly.
Source: locker.io
What Are Custodial Wallets?
Custodial wallets are a type of cryptocurrency wallet where a third party, usually a centralized entity like an exchange, holds and manages the private keys for the user. This means that users rely on the service provider to keep their funds safe and perform transactions rather than managing their private keys. Custodial wallets are often user-friendly and typically designed for beginners or individuals who prefer not to deal with the technical complexities of managing private keys directly.
Custodial wallets have several key components. First, they involve third-party control, where the service provider, such as an exchange or wallet service, holds the private keys. Second, users typically access their wallets through account-based access, using username and password credentials, much like logging into an online banking platform. In addition, custodial wallets often come with integrated services, including trading, staking, or lending.
Examples of custodial wallets include Coinbase and Kraken. Coinbase, one of the most popular exchanges in the U.S., offers a custodial wallet service where the platform manages the private keys. Its ease of use makes it a common choice for newcomers to the cryptocurrency space. Kraken, another popular U.S.-based exchange, provides a custodial wallet service with advanced features like staking and margin trading.
Benefits of Using a Custodial Wallet
- Ease of use: Custodial wallets are usually simple to set up and operate, making them appealing for individuals unfamiliar with cryptocurrency. Users typically do not need to manage private keys or worry about losing access to their funds due to key mismanagement.
- Security services: Exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken often have dedicated security teams, employing multi-factor authentication, cold storage, and insurance policies to protect user funds.
- Recovery options: If users lose access to their accounts, e.g., forgetting a password, custodial wallets typically offer support to recover account access through email verification or customer service.
Risks of a Custodial Wallet
- Lack of full control: Since the service provider holds the private keys, users generally do not have direct control over their funds. If the provider experiences technical issues, becomes insolvent, or restricts withdrawals, users may lose access to their assets.
- Counterparty risk: Users often must trust the custodian to manage their private keys securely. If the custodian is hacked or fails to implement adequate security protocols, the user’s funds could be compromised.
- Regulatory risks: Custodial wallets, often linked to centralized exchanges, are subject to regulatory oversight. Depending on the jurisdiction, governments may enforce KYC (know your customer) and AML (anti-money laundering) protocols or even freeze assets under certain conditions. This exposes users to the risk of having their funds confiscated or restricted.
Risk Management of Custodial Wallets
Effectively managing the risk of a custodial wallet involves several key strategies. First and foremost, choose a reputable service provider with a strong track record in security and customer service. Look for platforms that offer robust security measures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, and regular security audits. It’s also crucial to stay informed about the latest security practices and updates from your chosen provider.
Regularly monitor your account for any suspicious activity and set up alerts for unusual transactions. Diversifying your holdings across multiple wallets can also mitigate concentration risk, helping to ensure that a breach in one wallet doesn’t compromise all your assets.
Educate yourself about phishing attacks and other common scams targeting crypto users. Always verify the authenticity of communications from your wallet provider and avoid sharing sensitive information. Lastly, keep your login credentials secure and avoid using the same password across multiple platforms. By implementing these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk associated with using custodial wallets and protect your digital assets more effectively.
What Are Non-Custodial Wallets (Web3 Wallets)?
Non-custodial wallets, also known as Web3 wallets, provide users with sovereign control over their private keys, making the user responsible for the security and management of their digital assets. These wallets serve as tools that enable direct interaction with blockchain networks, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Key components of non-custodial wallets include private key ownership, where users are in control of their private keys and responsible for securing them; direct blockchain interaction, which facilitates engagement with decentralized applications (dApps) and other blockchain services such as staking or DeFi (decentralized finance); and self-custody, where the wallet software or hardware provides access to assets without storing private keys on a third-party server.
A crucial factor when using non-custodial wallets is blockchain network compatibility. Different wallets support different blockchain networks, so it is important that the wallet you choose is compatible with the assets you wish to manage. For instance, some wallets are specifically designed for Ethereum and its ERC-20 tokens, while others may support networks like Solana or bitcoin.
Notable examples of non-custodial wallets include both software and hardware options. Software wallets, also called hot wallets, like MetaMask are widely used wallets that interact with the Ethereum blockchain and dApps. Trust Wallet is a mobile-based wallet supporting multiple blockchains with easy integration with decentralized exchanges. Phantom, designed for the Solana blockchain, offers seamless integration with decentralized applications. On the hardware side, Ledger is a popular choice, providing cold storage for a wide variety of cryptocurrencies, requiring physical interaction to confirm transactions for enhanced security. At the same time, Tangem offers a unique card-based approach, making it a compact and secure way to store crypto assets offline.
A hot wallet and a cold wallet differ primarily in their connection to the internet. A hot wallet is connected to the internet, allowing users to quickly access their funds for transactions, trading, or everyday use. While convenient, this connection also makes hot wallets more vulnerable to online threats like hacking or phishing. In contrast, a cold wallet is entirely offline, providing higher security by keeping private keys and access to digital assets away from potential online attacks. Cold wallets are commonly used for long-term storage or large holdings that do not require the user to access the wallet for quick transactions frequently. Determining which type of wallet suits your digital asset holdings is important.
Benefits of Using a Non-Custodial Wallet
- Full control: Users have full ownership of their assets and private keys, meaning no third party can restrict access to funds or impose conditions on how they are used. However, multi-signature wallets and multi-party computation wallets do consider additional users that must prove ownership through signatures that require a majority of participants to agree to the transaction.
- Enhanced privacy: Non-custodial wallets generally do not require users to undergo KYC processes, allowing for greater anonymity when interacting with blockchain networks.
- Access to DeFi and dApps: Non-custodial wallets allow users to interact directly with dApps, enabling activities like decentralized trading, lending, borrowing, and yield farming, all without intermediaries.
Risks of a Non-Custodial Wallet
- Responsibility for security: Users must manage their own private keys. If a private key is lost or compromised, there is no way to recover the funds. This puts a heavy burden on users to implement good security practices, such as backing up seed phrases and using hardware wallets for large sums.
- No customer support: Unlike custodial wallets, non-custodial wallets offer no support in case of a mistake. If a user sends funds to the wrong address or loses their private key, the funds are unrecoverable.
- Technical complexity: Managing a non-custodial wallet can be intimidating for beginners. Understanding how blockchain transactions work, interacting with different blockchain networks, and safeguarding private keys require a learning curve.
Risk Management of Non-Custodial Wallets
Effectively managing the risk of a non-custodial wallet involves several key practices. First and foremost, safeguarding your private keys and secret phrases is crucial. These secret phrases, often 12 or 24 words long, depending on the wallet, can be used to gain access to your wallet if you need to recover your funds. Store them in a secure, offline location, such as a hardware or paper wallet, to protect against online threats. Regularly back up your wallet, private keys, and secret phrases to ensure you can recover your assets in case of loss or damage.
Use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) where possible to add an extra layer of security. Be cautious of phishing attempts and only interact with trusted websites and applications. Always verify the authenticity of the wallet software or hardware you use by downloading it from official sources. Keep your wallet software updated to benefit from the latest security patches and features. In addition, consider diversifying your holdings across multiple wallets to mitigate the risk of losing all your assets if one wallet is compromised.
Educate yourself continuously about the latest security practices and potential threats in the cryptocurrency space. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk associated with managing a non-custodial wallet and improve the safety of your digital assets.
| Self-Custody | Custodial | |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Control of Funds | ✔ Yes | ✖ No |
| Recovery of Funds if Seed Phrase Is Lost | ✖ No | ✔ Yes |
| Access to On-Chain dApps & DEXs | ✔ Yes | ✖ No |
| Offline Accessibility | ✔ Yes | ✖ No |
| KYC & AML Requirements | ✖ No | ✔ Yes |
| Ease of Use (No Need for Technical Competency) | ✖ No | ✔ Yes |
Conclusion
Both custodial and non-custodial wallets offer unique benefits and risks when managing cryptocurrencies. Custodial wallets provide ease of use and security services but require users to trust a third party with their private keys, potentially exposing them to counterparty and regulatory risk. On the other hand, non-custodial wallets give users full control over their assets and privacy but demand greater responsibility for security and technical management. By understanding the differences and implementing effective risk management strategies, users can better safeguard their digital assets.
If you have questions or need additional information, contact our Digital Assets team.
Forvis Mazars Private Client services may include investment advisory services provided by Forvis Mazars Wealth Advisors, LLC, an SEC-registered investment adviser, and/or accounting, tax, and related solutions provided by Forvis Mazars, LLP. The information contained herein should not be considered investment advice to you, nor an offer to buy or sell any securities or financial instruments. The services, or investment strategies mentioned herein, may not be available to, or suitable, for you. Consult a financial advisor or tax professional before implementing any investment, tax or other strategy mentioned herein. The information herein is believed to be accurate as of the time it is presented and it may become inaccurate or outdated with the passage of time. Past performance does not guarantee future performance. All investments may lose money.
